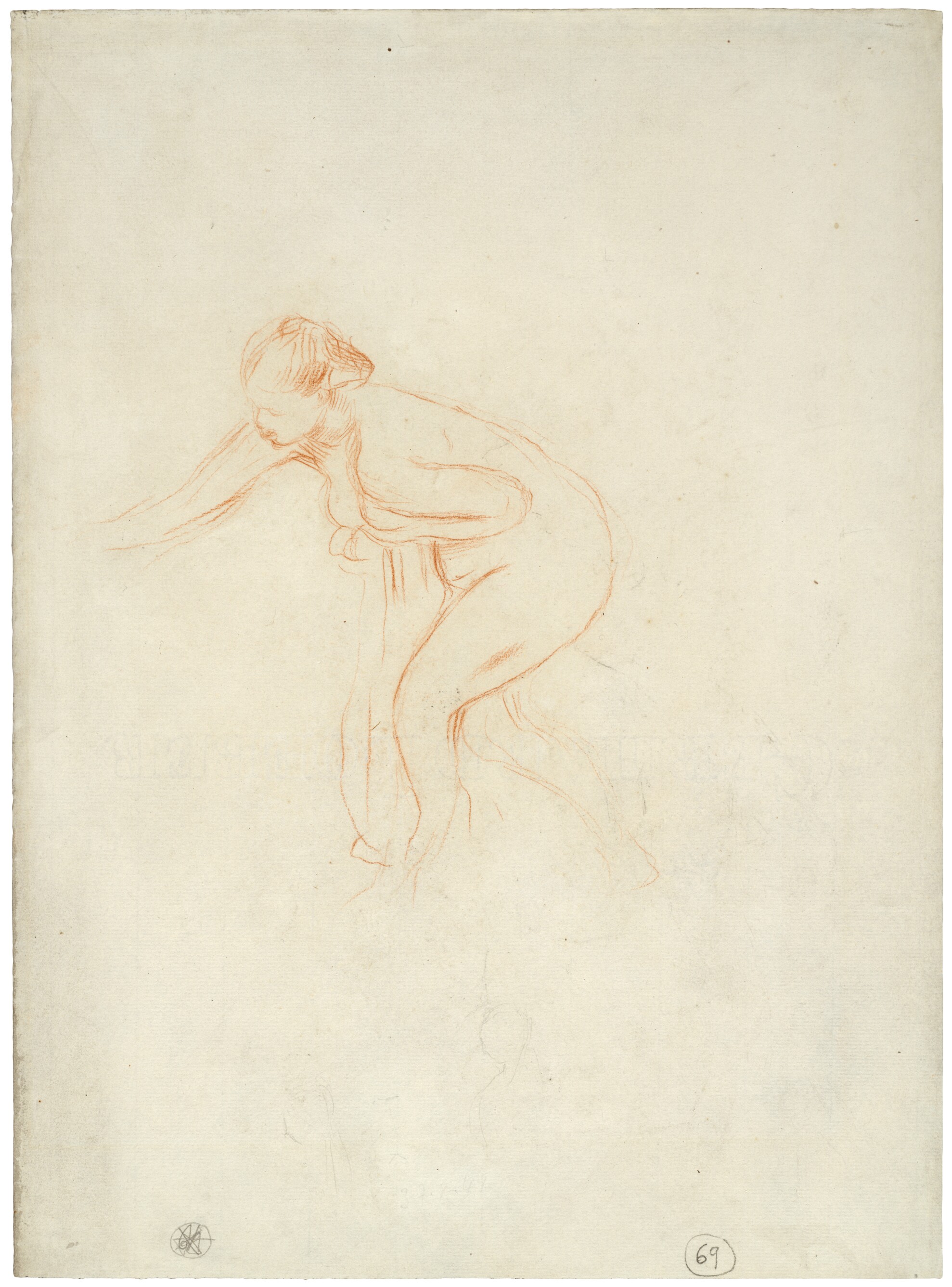
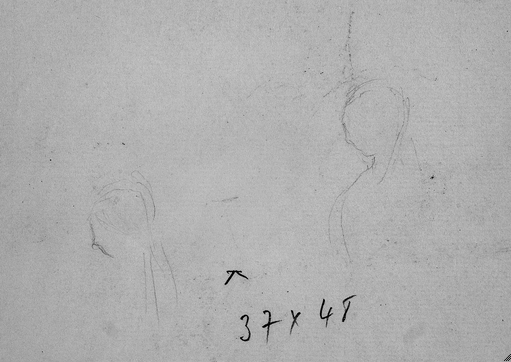Cat. 21
Bather
c. 1885
Red chalk, with traces of graphite, on cream laid paper; 427 × 314 mm
The Art Institute of Chicago, gift of Robert Allerton, 1937.18
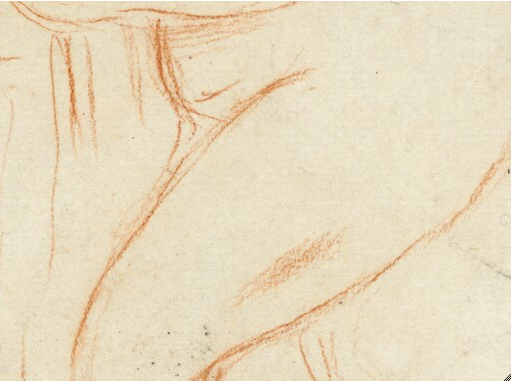
The subject of the female nude—the bather in particular—dominated much of Renoir’s work in the 1880s. This cursory sketch is an exercise in capturing physical movement: the woman leans forward as she bends down slightly, a towel clutched to her chest, one arm thrust forward as if to steady her balance. This is but one of many gestures that the artist explored during these years, as he developed his monumental work The Large Bathers (fig. 21.1 [Daulte 514; Dauberville 1292]). The present sheet does not connect with the Philadelphia canvas directly, but it may have helped Renoir to hone his ideas in the preparatory stages. The uncertainty of particular details conveys an experimental quality: the hesitant placement of the woman’s proper right leg, for instance, or the multiple attempts to situate the outstretched arm.
Executed in red chalk on a highly textured paper, the drawing appears in some respects timeless. Renoir’s choice of media was as historicizing as the theme; eighteenth-century draftsmen used red chalk frequently, and Renoir had a deep admiration for Rococo artists Jean-Antoine Watteau and François Boucher. The pose here also invites time-honored associations. Crouching as if to hide her body, the female figure recalls the main protagonist in the Biblical story of Susanna and the Elders (Dan. 13), depicted by artists as diverse as Tintoretto and Peter Paul Rubens in centuries past. The bather motif was also popular in the contemporary art of the era; it was a favorite with the Impressionists as well as with the more conservative artists who exhibited in the state-sponsored Salon.
Indeed, in some respects, the preference that this drawing reveals for sensual materials and subject matter reflects Renoir’s view that modern art should not always dwell on the harsher aspects of daily life. The artist’s son recalled that his father felt the need to “caress and stroke the motif.” This might explain the attention Renoir paid to details such as the dimpled thigh and upswept hair in a study where he chose not to resolve the hands and feet.
Nancy Ireson
Technical Report
Technical Summary
Renoir drew Bather right in the center of the cream-colored [glossary:laid] paper support using a relatively hard red chalk to create crisp, fine lines. He formed the fine figural lines with a minimum of long, fluid strokes. In some cases, the artist reinforced existing lines or used additional strokes to develop the bather’s form. This is most visible in her arms and legs. Renoir created volume with minimal shading. A few linear, hatched strokes form the neck and proper right shoulder (fig. 21.2), and a single broad stroke made by positioning the chalk at a slight angle to the support suggests a shadow in the proper left thigh (fig. 21.3). There is no blending of the chalk to create volume in the figure.
The drawing may have been taken from a sketchbook or album, as the sheet appears to have residual adhesive along its torn left edge. There are also smaller figural sketches in graphite at the center bottom of the sheet, most easily seen with the aid of infrared radiation (fig. 21.4). It is not possible to determine when the additional figures were placed on the sheet, although they do not appear to directly relate to the current subject.
Media and Support
Support Characteristics
Primary paper type
Cream, moderately thick, moderately textured laid paper.
Watermark
Gerhard Loeber (complete, horizontal orientation, through lower center of sheet) (fig. 21.5).
Chain line orientation and frequency
Vertical, 2.8–2.9 cm.
Laid line frequency
8–9 per cm.
Furnish
Uniform, without visible inclusions or colored fibers.
Formation
Even, possibly machine made.
Other characteristics
The paper exhibits a clean, straight cut along the right side; the remaining sides are edge-torn and have slight irregularities. There appear to be traces of adhesive residue along the left edge, possibly from a former binding in a sketchbook or block.
Dimensions
427 × 314 mm
Preparatory Layers
No artistic surface alterations or coatings are visible under normal conditions or magnification. Under ultraviolet (UV) illumination, there is a pale-yellow visible-light fluorescence that is characteristic of a light gelatin surface sizing.
Media Characteristics
The figure is drawn directly in red chalk; it is likely that a relatively hard, or possibly dampened, red chalk was used to create the crisp, fine figural lines. There is no stumping. Traces of graphite form smaller figures in the bottom area and stray marks to the right of the figure, most easily seen with the aid of infrared reflectography (fig. 21.4). There is no drawing media on the verso.
Compositional Development
No revisions or changes to the composition are visible under normal conditions or magnification. Some lines have been reinforced with a second stroke in the same red chalk.
Surface Treatment
No artistic surface fixatives or coatings are visible under normal conditions, UV illumination, or magnification. A light gelatin sizing is visible under UV illumination.
Condition History
The drawing was recently conserved to reduce significant surface soiling around the perimeter (including pronounced mat burn) and discoloration overall. In the upper left area, a large oval-shaped liquid stain, approximately 6.5 cm in diameter, was reduced. There was discolored residual adhesive along the left edge as well as surface undulations at the lower left edge, which suggest the sheet might have been formerly bound or attached to a secondary support along the left edge. Framer’s notations (37 × 48 at center bottom, in graphite) were reduced. On the verso, residual brush-applied adhesive and brown paper remnants from a former mount were reduced.
Kimberly Nichols
Provenance
Pierre Renoir (1885–1952), Paris.
Sent by Valentine Gallery, New York, to the Art Institute of Chicago, Jan. 25, 1937.
Sold by Valentine Gallery, New York, to the Art Institute of Chicago, Apr. 30, 1937.
Exhibition History
Chicago, Renaissance Society, University of Chicago, Original Drawings by Masters of the Sixteenth, Seventeenth, and Eighteenth Centuries and Artists of the Present Day, Jan. 9–31, 1940, no cat.
Exposition Park, Los Angeles County Museum, Pierre Auguste Renoir: 1841–1919, July 14–Aug. 21, 1955, cat. 103 (ill.); Civic Center, San Francisco Museum of Art, Sept. 1–Oct. 2, 1955.
Iowa City, University of Iowa, Art Department, Drawing and the Human Figure: 1400–1964, 1964, cat. 106.
Selected References
John Rewald, Renoir Drawings (H. Bittner, 1946), p. 19, no. 29 (ill.).
Harold Joachim and Sandra Haller Olsen, French Drawings and Sketchbooks of the Nineteenth Century, vol. 2 (Univesity of Chicago Press, 1979), p. 91, no. 5D10.
Guy-Patrice Dauberville and Michel Dauberville, Renoir: Catalogue raisonné des tableaux, pastels, dessins, et aquarelles, vol. 2, 1884–1892 (Bernheim-Jeune, 2009), p. 541, no. 1569 (ill.).
Other Documentation
Inscriptions and Distinguishing Marks
Recto
Number
Location: left bottom edge
Method: graphite
Content: 69 [within a circle marked out with intersecting lines]
Number
Location: right bottom edge
Method: graphite
Content: 69 [within a circle]
Mark
Location: left top edge
Method: black ink
Content: short vertical line
Verso
Stamp
Location: center
Method: brown ink
Content: The Art / Institute of / Chicago
Examination Conditions and Technical Analysis
Raking Visible Light
Support characteristics identified.
Transmitted Infrared (Fuji, 1.0–1.1 μm)
Watermark captured.
Transmitted Visible Light
Paper mold characteristics identified.
Ultraviolet-Induced Visible Fluorescence (365 nm)
Light surface size detected.
Infrared Reflectography (Fujifilm S5 Pro with X-Nite 1000B/2 mm filter [1.0–1.1 μm])
Traces of graphite drawing on the recto in lower right area and bottom examined and captured.
Stereomicroscopy (80–100×)
Media identified.
Image Inventory
The image inventory compiles records of all known images of the artwork on file in the Imaging Department and in the conservation and curatorial files in the Department of Prints and Drawings at the Art Institute of Chicago (fig. 21.6).